Table of Contents
Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) are transforming transportation, offering a cleaner alternative to gasoline-powered cars. At the core of an EV is its battery, which stores and supplies the energy needed to power the vehicle.
This guide will explain how EV batteries work, the different types, charging methods, lifespan, and environmental impact, using real-world examples of popular EVs.
1. What is an EV Battery?
An EV battery is a rechargeable energy storage system that powers an electric vehicle’s motor. Unlike traditional gas-powered cars that use lead-acid batteries, EVs rely on lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries, which offer:
✅ Higher energy density → Longer driving range
✅ Rechargeability → Unlike gasoline, you can “refuel” with electricity
✅ No emissions → Reduces environmental impact
🔹 Example EVs Using Li-ion Batteries:
- Tesla Model 3
- Nissan Leaf
- Hyundai Ioniq 5
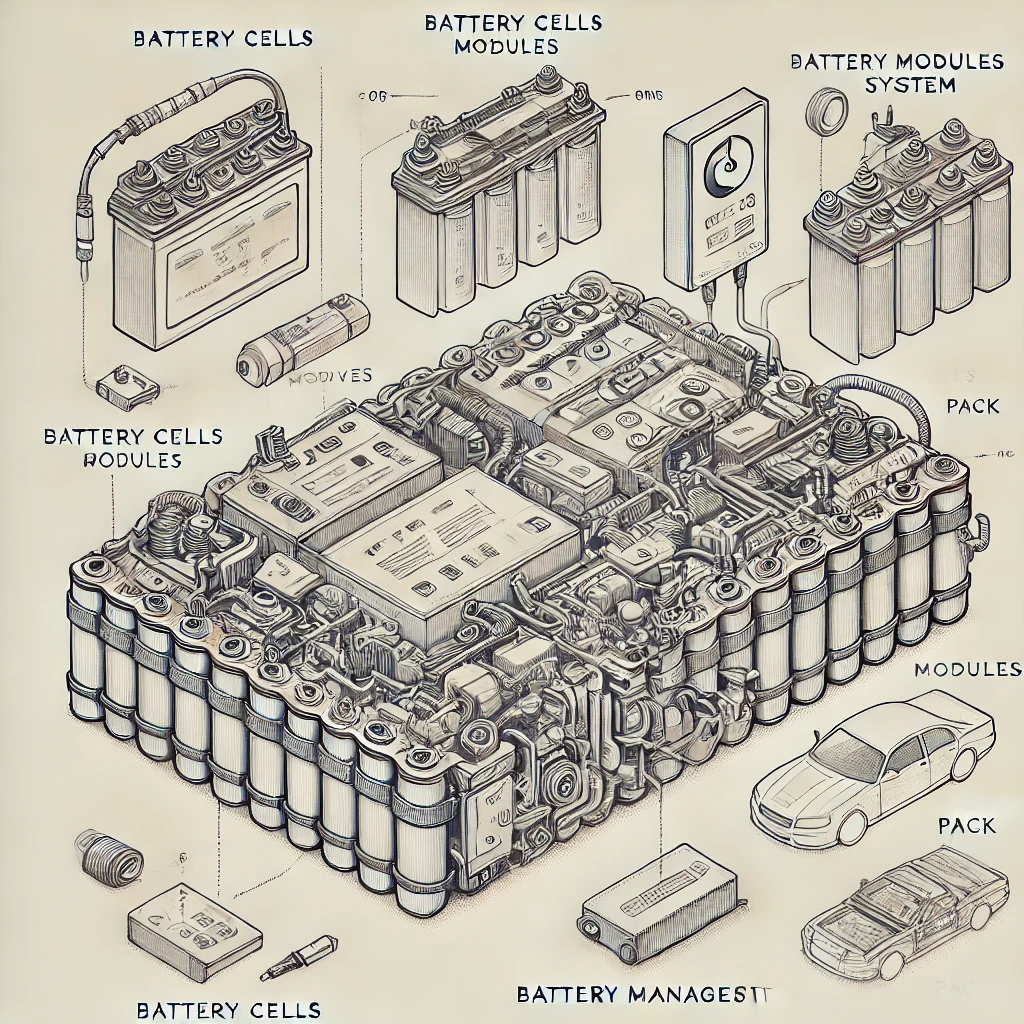
(An image showing a lithium-ion EV battery pack with cells, modules, and BMS.)
2. How EV Batteries Store and Deliver Energy
EV batteries store electrical energy chemically and release it as needed.
EV Battery Structure
🔹 Cells → The smallest unit, where chemical reactions store and release energy
🔹 Modules → Groups of cells packaged together for stability
🔹 Battery Pack → The full system that powers the EV
Battery Management System (BMS)
The BMS ensures efficiency and safety by:
✔️ Preventing overcharging and deep discharging
✔️ Managing temperature to avoid overheating
✔️ Balancing charge levels across all cells
🔹 Example EVs With Advanced BMS Technology:
- Tesla Model Y (Optimized thermal management)
- Porsche Taycan (800V battery system for ultra-fast charging)
Image: Diagram Showing EV Battery Pack & BMS Function
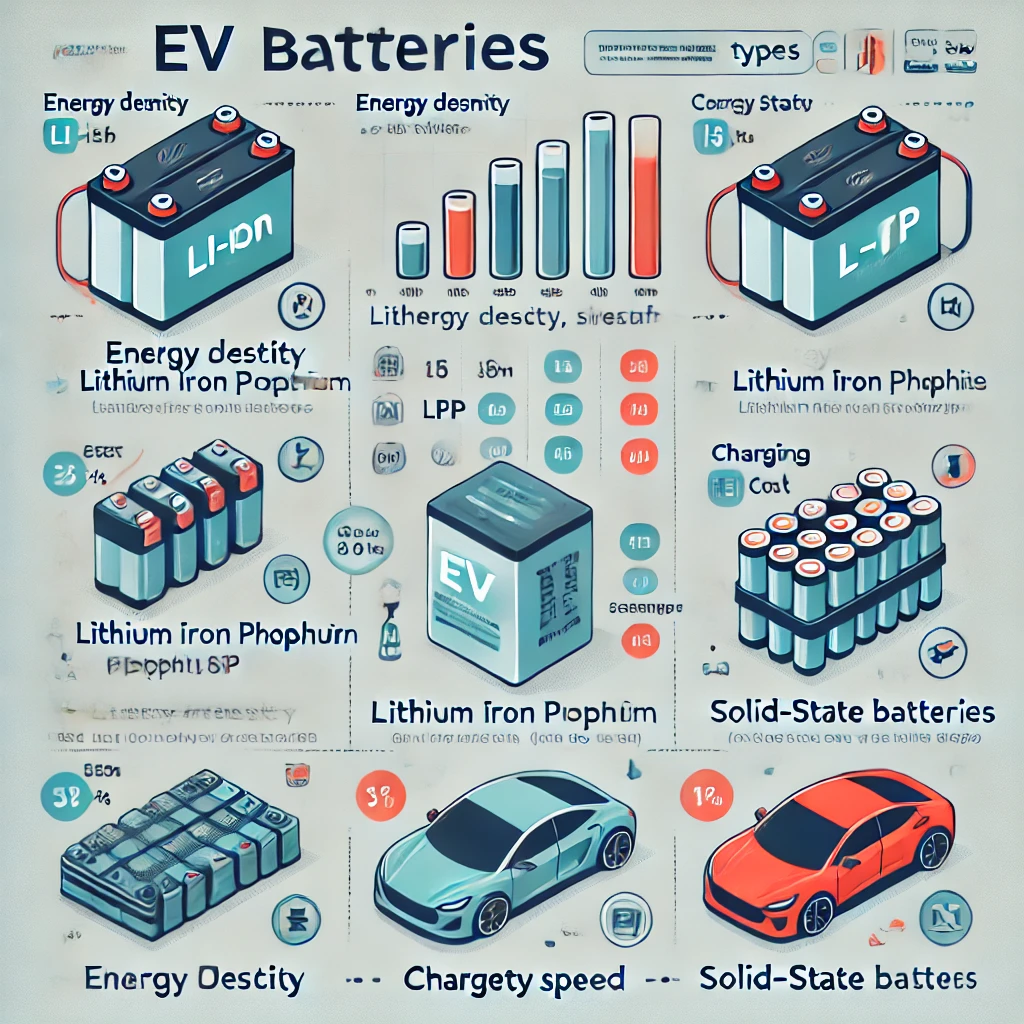
3. Types of EV Batteries
Different battery types affect an EV’s performance, lifespan, and cost.
1. Lithium-Ion (Li-ion) Batteries (Most Common)
✅ High energy density → Longer range
✅ Lightweight → Improves vehicle efficiency
✅ Fast charging → 30-60 minutes with DC fast chargers
🔹 Example EVs Using Li-ion Batteries:
- Tesla Model S Plaid (~400 miles range)
- Ford Mustang Mach-E (~312 miles range)
2. Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) Batteries
✅ More durable and lower fire risk
✅ Longer lifespan than standard Li-ion
✅ Cheaper to produce → Found in budget EVs
🔹 Example EVs Using LFP Batteries:
- Tesla Model 3 (Standard Range)
- BYD Atto 3
3. Solid-State Batteries (Future Technology)
✅ Higher energy density → More range per charge
✅ Faster charging → Less than 15 minutes
✅ Longer lifespan than Li-ion
🔹 Expected in:
- Toyota’s upcoming EVs (2027 launch)
- BMW iX future models
Image: Comparison Chart of Different EV Battery Types
4. Charging an EV Battery
EV batteries need regular charging, just like refueling a gas-powered car.
Types of EV Charging
⚡ Level 1 (Home Charging)
- Uses a standard 120V outlet
- Slowest (8-24 hours for a full charge)
⚡ Level 2 (Fast Home & Public Charging)
- Uses a 240V outlet (like a dryer plug)
- Charges most EVs in 4-8 hours
⚡ DC Fast Charging (Superchargers)
- Uses high-power chargers (50kW-350kW)
- Can charge 80% in 20-40 minutes
🔹 Example Fast-Charging EVs:
- Hyundai Ioniq 5 (10%-80% in 18 minutes)
- Lucid Air (300 miles charge in ~20 minutes)
Regenerative Braking: An Extra Energy Boost
EVs recover energy when braking, sending it back to the battery.
🔹 Example EVs with Strong Regenerative Braking:
- Hyundai Kona Electric
- Rivian R1T
Comparison of EV Charging Levels: Level 1 vs. Level 2 vs. DC Fast Charging
| Charging Level | Power Source | Voltage | Charging Speed | Best For | Example Charging Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Standard Home Outlet | 120V | Slowest (~3-5 miles per hour) | Overnight charging at home | ~40-50 hours for 250 miles (Tesla Model 3) |
| Level 2 | Home/Public Charger | 240V | Moderate (~15-30 miles per hour) | Daily charging at home or work | ~8-12 hours for 250 miles (Tesla Model 3) |
| DC Fast Charging | Public Superchargers | 400V-800V | Fastest (~100-250 miles in 15-30 min) | Long road trips and quick top-ups | ~20-40 minutes for 250 miles (Tesla Supercharger) |
5. Battery Life and Maintenance
EV batteries are designed to last 8-15 years before needing replacement.
Factors Affecting Battery Health
⚠️ Extreme Temperatures → Too hot/cold can degrade the battery
⚠️ Frequent DC Fast Charging → Can reduce lifespan over time
⚠️ Depth of Discharge → Keeping charge levels between 20-80% is ideal
Tips to Extend Battery Life
✅ Use Level 2 charging instead of DC fast charging when possible
✅ Avoid keeping the battery at 100% charge for long periods
✅ Park in shaded or climate-controlled areas
🔹 Example EVs With Long-Lasting Batteries:
- Toyota bZ4X (Special cooling system for longevity)
- Chevy Bolt EV (Reported battery lifespan over 200,000 miles)
Image: Best Practices to Extend EV Battery Life
6. Environmental Impact and Recycling
EVs reduce carbon emissions, but battery production has an environmental footprint.
Are EV Batteries Sustainable?
✔️ EVs produce fewer lifetime emissions than gas-powered cars
✔️ Battery technology is improving to reduce reliance on rare minerals
Battery Recycling & Second Life Applications
🔄 Recycling Programs → Companies recover materials like lithium and cobalt
🔄 Second-Life Use → Old EV batteries power homes & solar energy storage
🔹 Example Companies Leading Battery Recycling:
- Tesla & Redwood Materials (Battery material recovery)
- Nissan LEAF’s old batteries → Used in solar farms
Image: EV Battery Recycling Process
Final result of article
EV batteries are the heart of electric vehicles, offering a clean, efficient alternative to gasoline. As technology advances, EVs will have longer range, faster charging, and more sustainable battery solutions.
🔹 Key Takeaways:
✅ Lithium-ion batteries dominate, but solid-state is the future
✅ Charging time varies (home chargers are slow, DC fast chargers are quick)
✅ Battery life depends on temperature, charging habits & usage
✅ Recycling & second-life solutions are improving sustainability
By understanding how EV batteries work and how to care for them, you can make informed decisions about owning an electric vehicle and contributing to a greener planet!
also read


